Metadata Router Pipeline
Overview
The Metadata Router Pipeline routes documents to different paths based on metadata values.
It evaluates conditions defined on document metadata and directs each document to the matching route. This pipeline is commonly used after parsing, extraction, or classification, when metadata is available for decision-making.
What It Does
- Accepts one or more documents as input
- Evaluates metadata-based conditions
- Routes documents to the corresponding rule output
- Enables conditional branching in agent workflows
Using the Metadata Router Pipeline
Add to DocProcessorAgent
- Open Pipelines
- Select Metadata Router Pipeline
- Drag it into DocProcessorAgent
- Place it after pipelines that populate metadata
Create Routing Rules
Routing rules determine how documents are matched and routed based on document metadata.
Rules are applied only to the list of input documents; the pipeline finds documents whose metadata matches a rule and routes only those documents to downstream pipelines.
Rules use OR logic: if any condition is true, the document matches the rule.
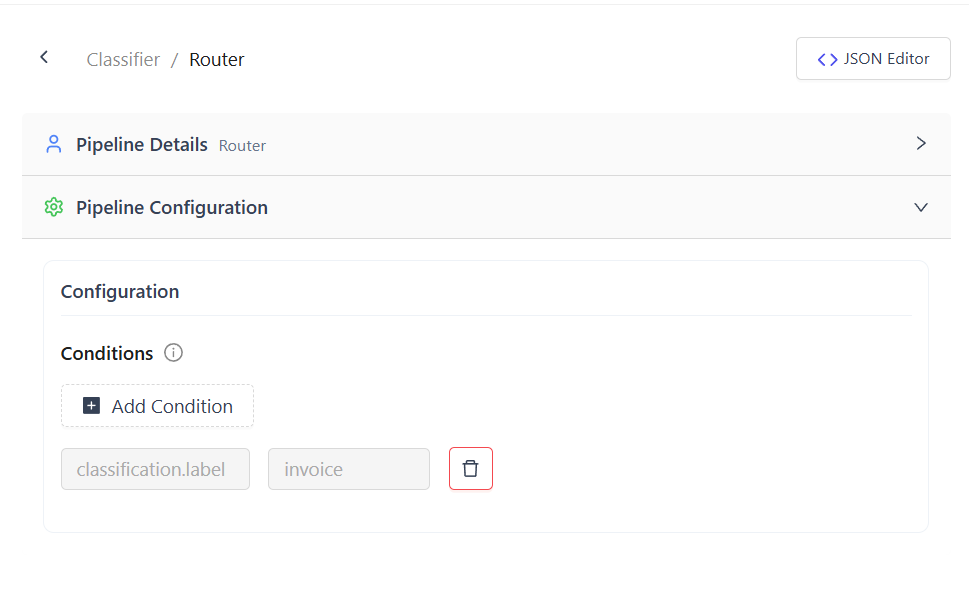
Condition Format
- Specify a metadata field and value
- For nested fields, use dot notation
Example:
Field name: classification.label
Value: forms
After the Email Parser Pipeline, metadata includes:
type = email_contentfor email bodiestype = email_attachmentfor attachments
After the Classifier Pipeline, classification.label is available for routing.
Output
- Documents are returned under the matching rule name
- If no rule matches, the pipeline returns an error
- Routed documents can be forwarded to writer pipelines, workflows, or agents
Common Use Cases
- Routing email content vs attachments
- Branching workflows based on classification labels
- Conditional document processing based on metadata
Summary
The Metadata Router Pipeline enables metadata-driven routing in document workflows.
By defining simple OR-based rules on metadata fields, it allows flexible branching and targeted downstream processing.