Assistant Agent
Overview
The Assistant Agent is an LLM-powered agent that understands user input, reasons over conversation context, and generates intelligent responses.
It supports no-code configuration, allowing you to attach model clients, guardrails, tools, workbenches, and memory to control behavior.
note
- Tools are executed via workbenches (Static or MCP-enabled)
- Custom tools can be written in Python directly from the configuration UI
Adding the Assistant Agent
Actions
- Open Team Builder
- Ensure the team type is set to Agent
- Drag and drop Assistant Agent into the canvas
Attaching a Model Client
Actions
- Drag a Model Client (e.g., Azure OpenAI)
- Configure credentials and deployment
- Connect it to the Assistant Agent
Notes
- A Model Client is mandatory
- Only one model client can be attached
Enabling Guardrails (Optional)
Actions
- Drag a Guardrail Component into the agent
- Configure entities to mask (optional)
- Enable Unmask LLM Output if required
Behavior
- User input is always masked before LLM execution
- Output masking is optional
- Original values are restored based on configuration
Configuring Tools & Workbenches
Tools are executed through workbenches, which act as the agent’s runtime environment for tools.
Supported workbench types:
- Static Workbench – Local Python tools
- MCP-enabled Workbench – Remote / managed execution
Adding Custom Tools to an Agent
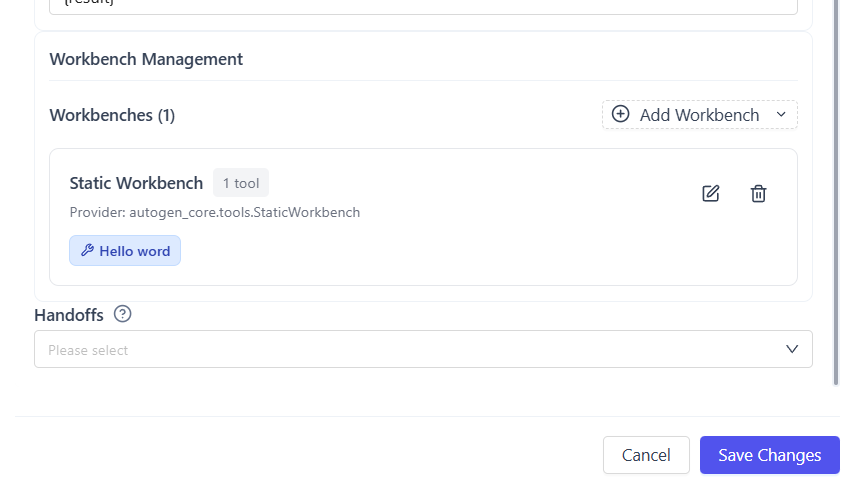
Step 1: Add a Static Workbench
- Open Assistant Agent → Configuration
- Click Add Workbench
- Choose Static Workbench
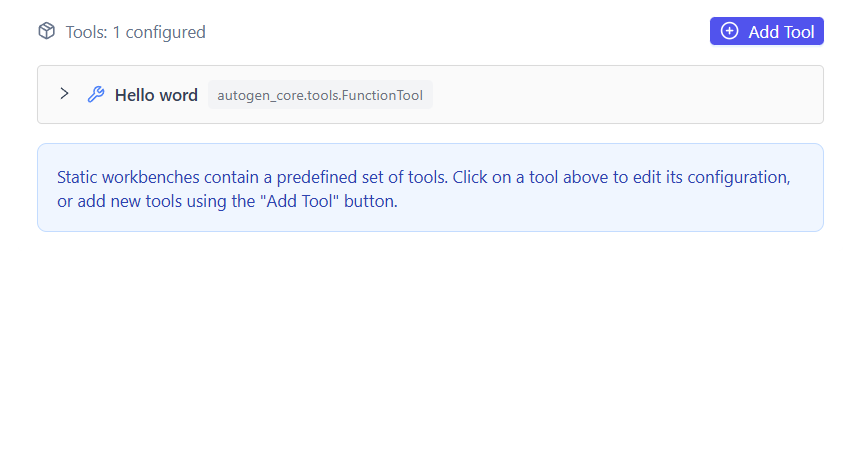
Step 2: Open the Workbench Editor
- Open the created Static Workbench
- Click Edit
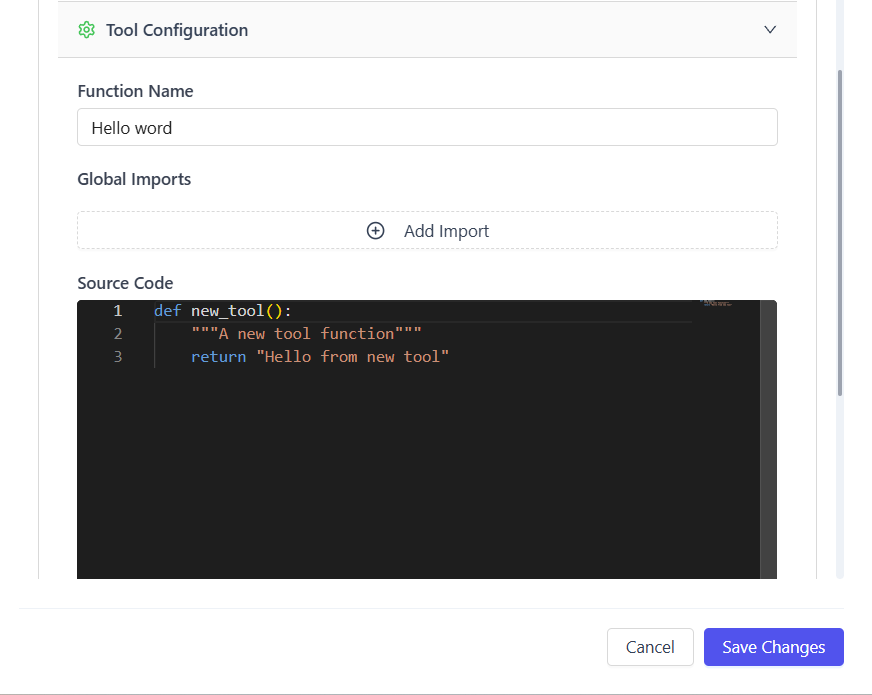
Step 3: Add a Tool
- Click Add Tool
- Provide the Python code and required configuration
Each tool typically defines:
- Tool name
- Input arguments schema
- Executable Python logic
Once saved, the tool becomes immediately available to the agent.
note
- Multiple tools can exist in a single workbench
- Multiple workbenches can be attached to one agent
- Supports iterative tool calls, streaming output, and error handling
- MCP workbenches enable remote and managed execution
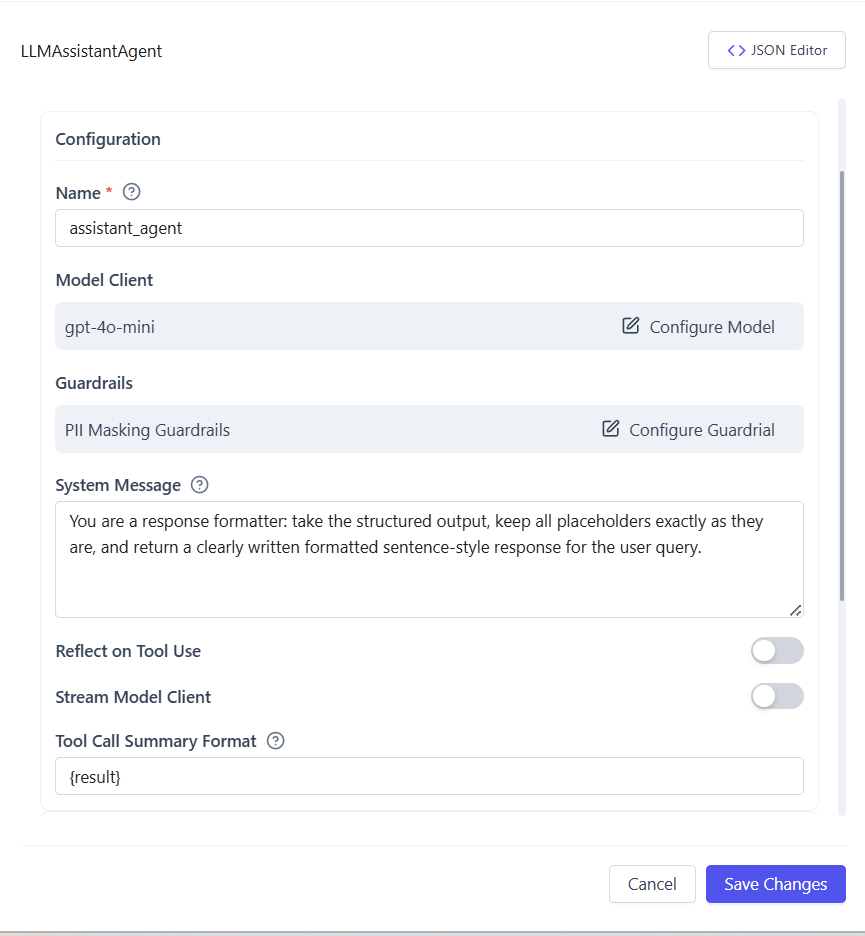
Configuring Agent Behavior
Settings
- Agent name and description
- System prompt (LLM instructions)
- Streaming response mode
Capabilities and Use Cases
Key Capabilities
- LLM-based reasoning and responses
- Context-aware conversations
- Secure PII handling via guardrails
- Static and MCP workbench integration
- Custom Python tool execution
- Streaming and non-streaming output
- No-code configuration
Common Use Cases
- Conversational assistants
- Enterprise Q&A bots
- Secure document and invoice analysis
- Customer support agents
- Internal knowledge assistants
Summary
The Assistant Agent enables powerful LLM-driven interactions with optional guardrails, workbench-based tools, and custom Python integrations, making it suitable for both simple chatbots and complex, tool-driven workflows.