QueryAssistantAgent
Description: An agent that uses a Haystack retriever pipeline to fetch relevant documents for a query using RAG.
Overview
QueryAssistantAgent is a data retrieval–focused agent designed to understand English (natural language) queries and fetch relevant data from multiple backend sources using a configurable pipeline architecture.
It acts as a query-to-data bridge, converting user intent into structured retrieval operations across vector stores, databases, APIs, and search engines.
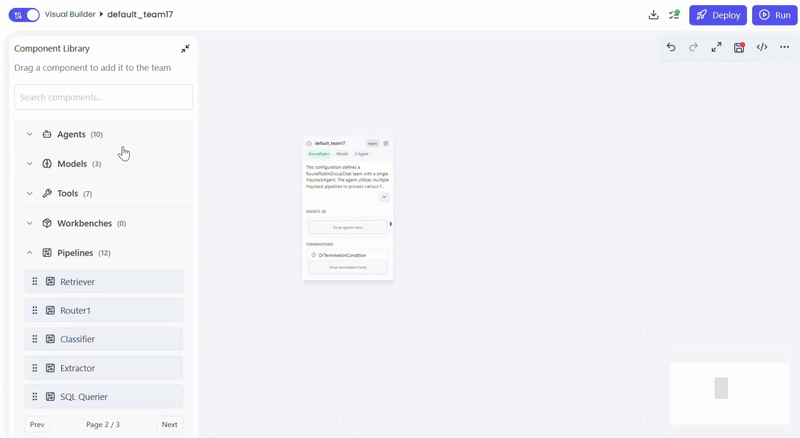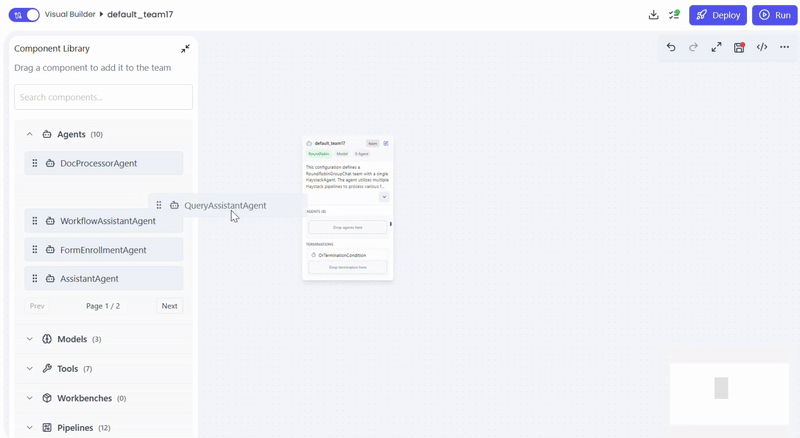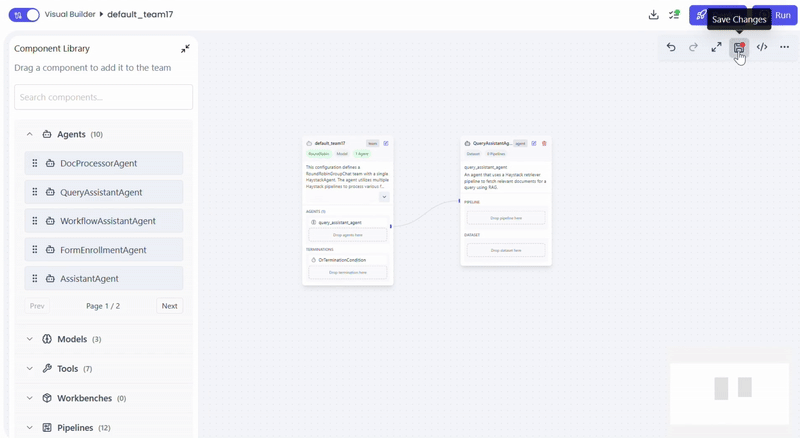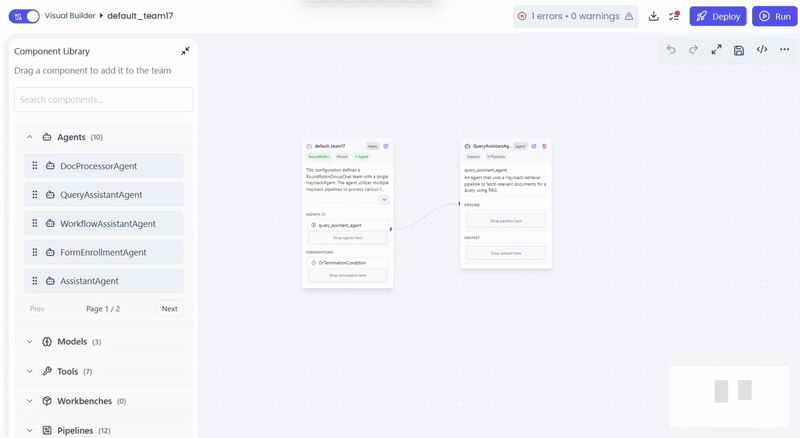
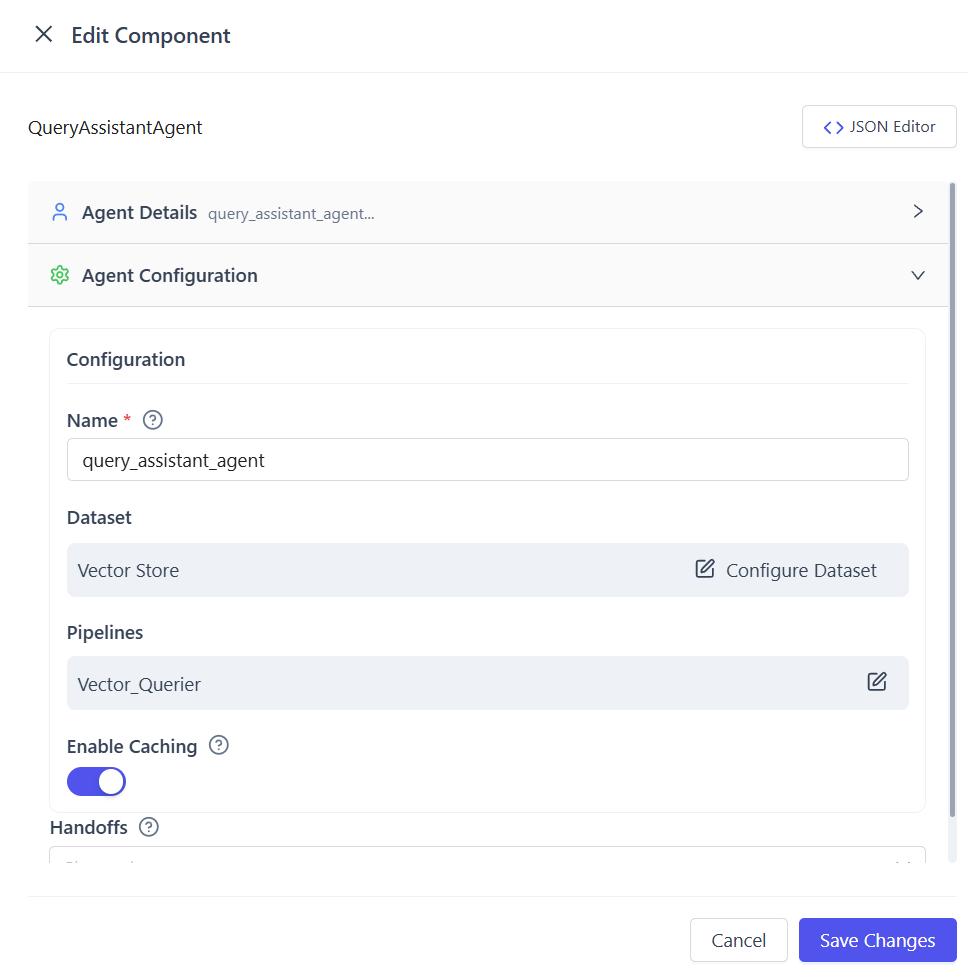
Create the QueryAssistantAgent
- Open Team Builder
- Select Agent as the team type
- Drag and drop QueryAssistantAgent into the canvas
- Save the agent configuration
Configure Supported Datasets
Attach one dataset that the agent can query.
Actions
- Drag dataset into QueryAssistantAgent
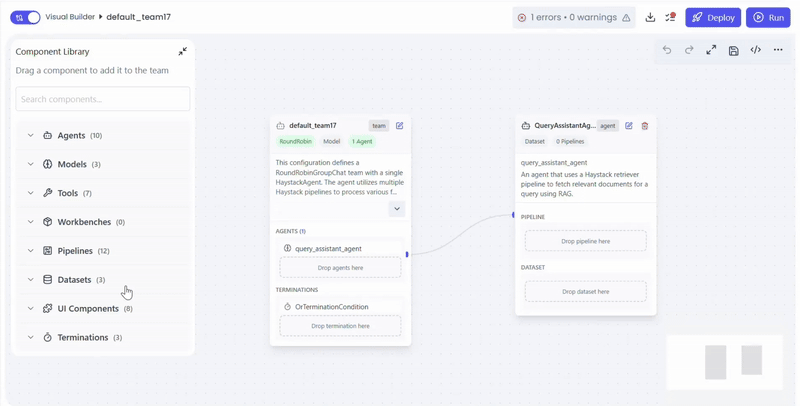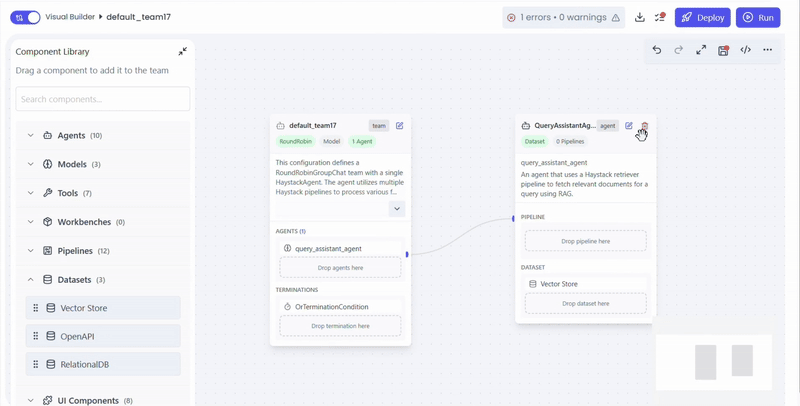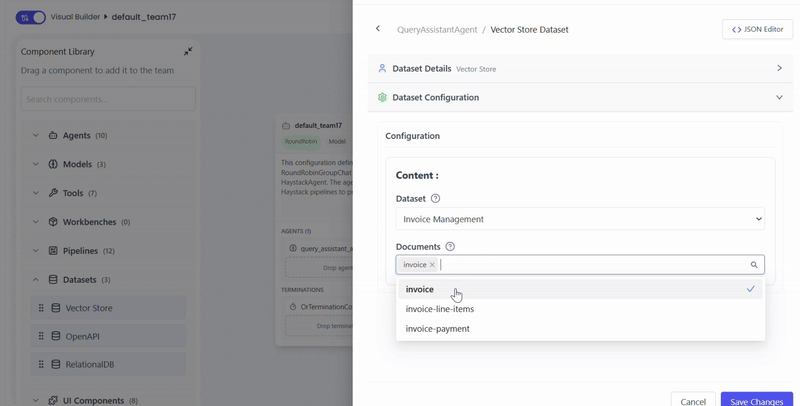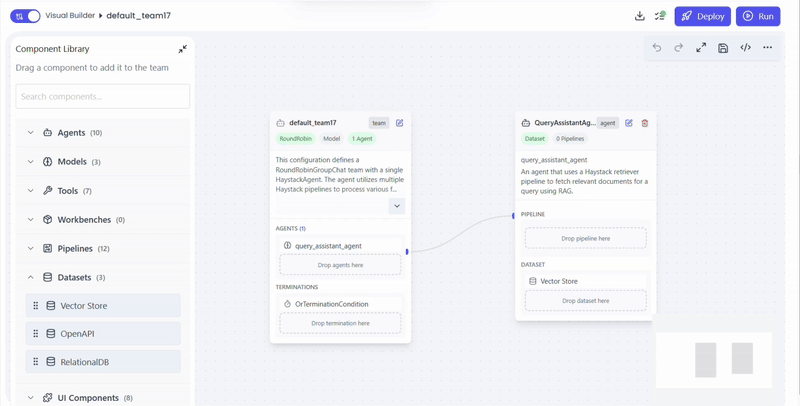
- Select dataset and document source
Available Dataset Options
- Vector Store
- Embedding-based document storage and Non Vector data storage
- Used with Retriever Pipeline or VectorQuerier Pipeline
- Relational Database
- SQL-based structured data
- Used with SQL Query Pipeline
- OpenAI / External APIs
- Dynamic or external knowledge sources
- Used with OpenAI Pipeline
You can attach multiple documents simultaneously.
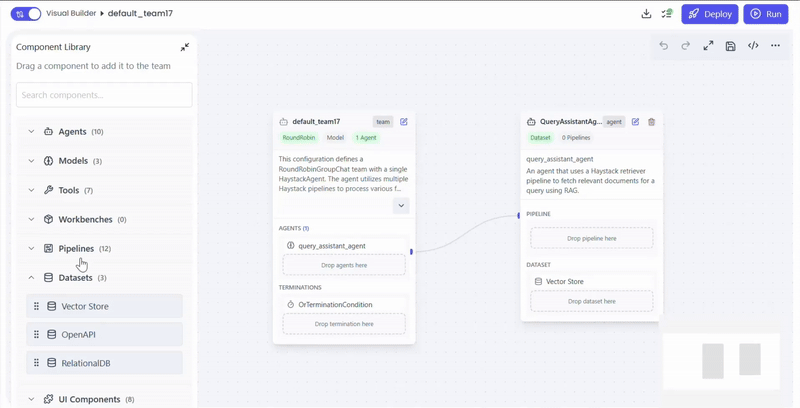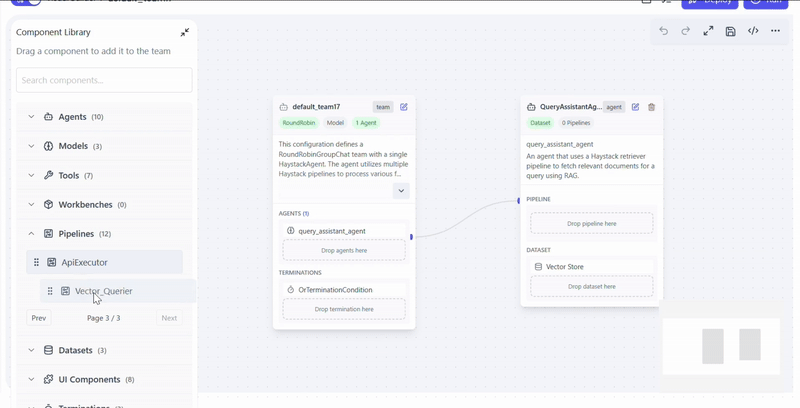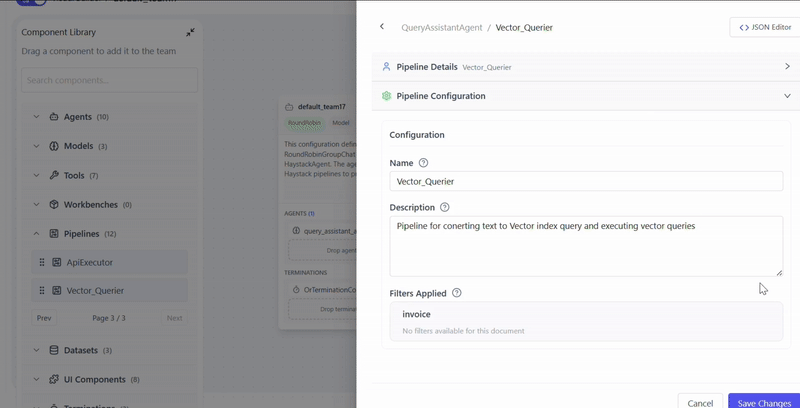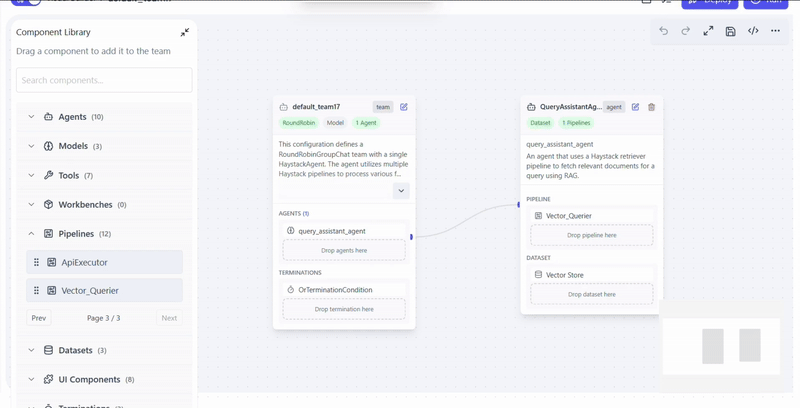
Configure Pipelines
Select the retrieval pipeline(s) based on your data source and use case.
Actions
- Drag pipeline into QueryAssistantAgent
- configure pipeline
Pipeline Selection
- Retriever Pipeline
- Semantic search over vectorized data
- VectorQuerier Pipeline
- Filtered or metadata-based queries on Elasticsearch
- OpenAI Pipeline
- Reasoning, enrichment, or API-based data retrieval
- SQL Query Pipeline
- Structured queries against relational databases
Pipelines can be enabled individually .
(Optional) Enable Cache
- Toggle Enable Cache in the agent configuration
- Save the settings
When Cache Is Enabled
- First query result is stored
- Identical or equivalent future queries are served from cache
- Improves performance and reduces backend load
Provide an English Query
Send a natural language query to the agent, for example:
- “Show unpaid invoices from last month”
- “Find documents related to vendor contracts”
- “Get total transactions grouped by customer”
Best Practices
- Use Retriever Pipeline for semantic document search
- Use VectorQuerier or SQL Pipeline for structured reporting
- Combine pipelines when both context and structure are required
- Enable cache for frequently repeated queries
Supported Use Cases
-
Natural Language Search
Query documents, records, or databases using plain English without writing queries. -
Semantic Document Retrieval
Find contextually relevant documents, embeddings, or knowledge base entries using vector search. -
Structured Data Lookup
Retrieve invoices, logs, transactions, or reports from Elasticsearch or relational databases. -
Data Enrichment & Reasoning
Use the OpenAI Pipeline to enrich retrieved data or generate insights using LLM reasoning. -
High-Frequency Query Optimization
Enable caching to speed up repeated or similar queries while reducing backend load. -
Agent-to-Agent Workflows
Act as a retrieval layer that feeds clean, normalized data to downstream agents or automation flows.
When to Use QueryAssistantAgent
- When users query data using natural language (English queries)
- When multiple data sources must be accessed through a single agent
- When both semantic (vector) search and structured data retrieval are required
- When performance optimization through caching is beneficial
- When retrieved data must be passed to downstream agents or workflows
Summary
QueryAssistantAgent is a natural language–driven retrieval agent that interprets English queries, selects and executes the appropriate pipeline, and retrieves data from one or more configured datasets such as vector stores, relational databases, or external APIs. It supports multiple pipelines—including Retriever, VectorQuerier, OpenAI, and SQL Query pipelines—which can be used individually or combined to handle both semantic and structured searches. The agent aggregates and normalizes results into a consistent response and optionally uses caching to improve performance by reusing results for repeated or equivalent queries, making it well suited for search, analytics, and intelligent data discovery workflows.